The human body, a marvel of biological engineering, continues to captivate scientists and researchers with its complexity and adaptability. As we advance into 2024, our understanding of the human body has deepened, revealing astonishing facts about its functions, capabilities, and mysteries. This article explores some of the most incredible and up-to-date facts about the human body, showcasing the marvels of modern science and medicine.
1. The Human Body Contains Around 37.2 Trillion Cells
Recent estimates suggest that the human body is made up of approximately 37.2 trillion cells. Each of these cells plays a unique role in maintaining bodily functions, from providing structural support to facilitating biochemical processes. This immense number underscores the complexity and efficiency of the human body, which operates as a highly coordinated system of cells working in harmony.
2. The Brain Can Generate New Neurons Throughout Life
For many years, it was believed that the brain could not produce new neurons after a certain age. However, recent research has demonstrated that neurogenesis, or the formation of new neurons, continues throughout life, particularly in the hippocampus, a region associated with learning and memory. This discovery highlights the brain’s remarkable plasticity and its ability to adapt and grow even in adulthood.
3. Your Body’s Microbiome Outnumbers Human Cells
The human body is host to a vast array of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, collectively known as the microbiome. Estimates suggest that these microbial cells outnumber human cells by a ratio of about 1.3 to 1. The microbiome plays a crucial role in digestion, immune function, and overall health, emphasizing the importance of these tiny inhabitants in our daily lives.
4. Your Skin is a Remarkable Organ
The skin is not only the largest organ in the human body but also a highly versatile one. It serves as a protective barrier against environmental hazards, regulates temperature, and facilitates the sensation of touch. Additionally, the skin can regenerate rapidly; it replaces itself roughly every 27 days, ensuring that it remains effective in its protective role.
5. The Human Body Can Produce Its Own Painkillers
The human body has a natural ability to produce pain-relieving chemicals known as endorphins. These neurotransmitters are released in response to pain, stress, and physical exercise, helping to reduce discomfort and enhance well-being. Endorphins bind to opioid receptors in the brain, providing a natural pain relief mechanism and contributing to the “runner’s high” experienced during intense physical activity.
6. The Heart Beats About 100,000 Times a Day
The human heart is an extraordinary organ that works tirelessly to pump blood throughout the body. On average, it beats approximately 100,000 times a day, circulating about 7,570 liters (2,000 gallons) of blood. This continuous effort ensures that oxygen and nutrients are delivered to tissues and organs, highlighting the heart’s vital role in sustaining life.
7. The Human Body Can Detect Over 1 Trillion Different Scents
The sense of smell, mediated by the olfactory system, is incredibly sensitive and versatile. Recent research has revealed that the human nose is capable of detecting and distinguishing over 1 trillion different scents. This remarkable olfactory capacity plays a crucial role in taste, memory, and emotional experiences, demonstrating the complexity of sensory perception.
8. Your Bones Are Constantly Renewing Themselves
Bone tissue is not static; it undergoes continuous remodeling throughout life. Every year, approximately 10% of the bone mass in the human body is replaced through a process involving osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) and osteoclasts (bone-resorbing cells). This dynamic process ensures that bones remain strong and healthy, adapting to changes in stress and activity levels.
9. The Human Body Generates About 1 to 1.5 Quarts of Saliva Each Day
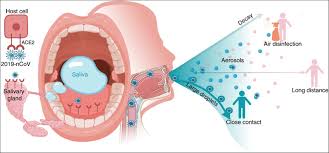
Saliva is essential for digestion, oral health, and the maintenance of a balanced oral microbiome. On average, the human body produces between 1 to 1.5 quarts of saliva each day. This fluid contains enzymes that aid in the breakdown of carbohydrates, lubricates the mouth for easier swallowing, and helps protect teeth and gums from harmful bacteria.
10. The Body’s Blood Vessels Could Circle the Earth Twice
The human circulatory system is an intricate network of blood vessels that includes arteries, veins, and capillaries. If laid end-to-end, the total length of these blood vessels would stretch approximately 100,000 kilometers (62,000 miles), which is enough to circle the Earth twice. This extensive network ensures that blood reaches every cell in the body, facilitating the exchange of nutrients and waste products.
11. The Human Eye Can Distinguish Over 10 Million Colors
The human eye is capable of perceiving a vast range of colors thanks to the presence of three types of cone cells in the retina, each sensitive to different wavelengths of light. Recent studies have estimated that the human eye can distinguish over 10 million different colors, demonstrating the remarkable precision of visual perception and color differentiation.
12. Your Gut Contains a “Second Brain”
The enteric nervous system (ENS), often referred to as the “second brain,” is a complex network of neurons located in the lining of the gastrointestinal tract. The ENS is capable of operating independently of the central nervous system and plays a crucial role in regulating digestive processes, mood, and overall well-being. This system’s significant influence on gut health and mental health highlights the deep connection between the brain and digestive tract.
13. The Human Body Produces About 2 to 3 Pints of Sweat Per Day
Sweating is a critical process for regulating body temperature and maintaining homeostasis. On average, the human body produces between 2 to 3 pints (1 to 1.5 liters) of sweat each day. This process helps cool the body through evaporation and plays a role in detoxification, demonstrating the body’s efficiency in maintaining internal balance.
14. The Tongue is Covered with Thousands of Taste Buds
The human tongue is equipped with approximately 8,000 to 10,000 taste buds, which are responsible for detecting various tastes such as sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami. These taste buds are distributed across the tongue’s surface, and they play a crucial role in flavor perception and appetite regulation.
15. The Human Body Has a Unique Biometric Identifier
No two individuals have the same fingerprint, and the uniqueness of fingerprints is a powerful biometric identifier. Recent studies have shown that fingerprints are formed in the womb and remain unchanged throughout life, making them a reliable method for personal identification and security.
Conclusion
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of the human body in 2024, we continue to uncover remarkable facts that showcase its complexity and adaptability. From the incredible capacity of the brain to the continuous renewal of bones and the vast network of blood vessels, the human body remains an astonishing testament to biological engineering. Understanding these amazing facts not only enhances our appreciation for the human body but also underscores the importance of ongoing research in uncovering new and fascinating aspects of human health and physiology.