The human brain, often described as the most complex organ in the body, is a marvel of biological engineering and cognitive capabilities. Despite decades of research, scientists are still uncovering new and astonishing details about how this incredible organ works. In this article, we will delve into some of the most mind-blowing facts about the human brain, shedding light on its mysteries and highlighting its remarkable functions.
1. The Brain’s Complexity is Unmatched

The human brain is an intricate network of approximately 86 billion neurons, each forming thousands of synaptic connections with other neurons. This network creates an estimated 100 trillion synaptic connections, far surpassing the number of stars in the Milky Way galaxy. This immense complexity allows the brain to process and store vast amounts of information, making it the most sophisticated organ in the human body.
2. Brain Activity Consumes a Significant Amount of Energy
Despite accounting for only about 2% of the body’s weight, the human brain consumes around 20% of the body’s energy. This high energy consumption is due to the brain’s constant activity and its need to maintain the electrical signals transmitted between neurons. This energy is primarily used for maintaining cognitive functions, processing sensory information, and regulating bodily functions.
3. Neuroplasticity: The Brain’s Ability to Adapt
One of the most fascinating aspects of the human brain is its ability to adapt and reorganize itself through a process known as neuroplasticity. Neuroplasticity allows the brain to form new neural connections throughout life, enabling it to adjust to new experiences, learn new skills, and recover from injuries. This ability is particularly pronounced during childhood but continues to be a vital part of brain function in adulthood.
4. The Brain is Capable of Reproducing Brain Cells
For many years, it was believed that adults could not produce new brain cells. However, research has shown that neurogenesis, the process of generating new neurons, does occur in specific areas of the brain, such as the hippocampus, which is crucial for memory and learning. Factors such as physical exercise, a healthy diet, and cognitive stimulation can enhance neurogenesis and support brain health.
5. The Human Brain is Highly Plastic in Response to Learning
The concept of brain plasticity extends to learning and memory. When we learn new skills or information, the brain creates and strengthens neural pathways. For example, learning to play a musical instrument or speak a new language involves the development of new neural circuits and the strengthening of existing ones. This adaptability underscores the brain’s remarkable capacity for growth and change.
6. The Brain Processes Information at an Astonishing Speed
The human brain is capable of processing information incredibly quickly. Neurons transmit electrical signals at speeds of up to 120 meters per second (approximately 270 miles per hour). This rapid transmission allows for near-instantaneous responses to stimuli, facilitating quick decision-making and reflexes.
7. Dreams Can Help with Problem-Solving and Creativity
During the REM (rapid eye movement) stage of sleep, the brain is highly active and experiences vivid dreams. Research suggests that dreaming may play a role in problem-solving and enhancing creativity. The brain’s ability to process information and make novel connections while dreaming can lead to innovative ideas and solutions that may not be readily apparent during waking hours.
8. The Brain’s Structure Reflects Its Functions
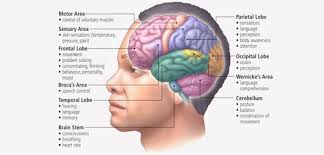
Different regions of the brain are specialized for various functions. For instance, the occipital lobe is primarily responsible for visual processing, while the frontal lobe is involved in executive functions such as decision-making, planning, and problem-solving. The brain’s structure is intricately linked to its functions, with each area contributing to overall cognitive and motor capabilities.
9. The Brain is Highly Susceptible to Environmental Influences
Environmental factors, such as stress, diet, and exposure to toxins, can significantly impact brain health and function. Chronic stress, for example, can negatively affect memory and cognitive performance, while a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids can support brain health. The brain’s sensitivity to environmental influences underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle for optimal cognitive function.
10. The Brain’s Ability to Predict the Future
One of the brain’s remarkable abilities is its capacity to anticipate future events. The brain constantly generates predictions based on past experiences and sensory input. This predictive capability allows us to make quick decisions and respond to potential threats before they occur. The brain’s anticipatory functions are essential for survival and daily functioning.
11. The Brain’s Electrical Activity Can Be Measured
The electrical activity of the brain can be measured using an electroencephalogram (EEG), which records brain wave patterns. These patterns, such as alpha, beta, delta, and theta waves, correspond to different states of consciousness and mental activities. EEGs are valuable tools in diagnosing neurological conditions, studying brain function, and understanding various cognitive processes.
12. The Brain’s Capacity for Memory Storage is Enormous
The brain has an extraordinary capacity for storing information, with estimates suggesting it can hold up to 2.5 petabytes of data. This vast storage capacity allows us to retain a lifetime of memories, experiences, and knowledge. The brain’s ability to organize and retrieve this information is crucial for learning, decision-making, and personal identity.
13. Emotions Have a Profound Impact on Brain Function
Emotions play a significant role in influencing brain function and overall well-being. The limbic system, which includes structures such as the amygdala and hippocampus, is responsible for processing emotions and memory. Positive emotions can enhance cognitive performance and resilience, while negative emotions can impair cognitive function and contribute to mental health issues.
14. The Brain’s Left and Right Hemispheres Have Specializations
The human brain is divided into two hemispheres, each with specialized functions. The left hemisphere is typically associated with language, analytical thinking, and logical reasoning, while the right hemisphere is linked to creativity, spatial awareness, and holistic thinking. Although both hemispheres work together, their specialized functions contribute to a wide range of cognitive abilities.
15. The Brain Continues to Develop Throughout Adulthood
Contrary to the old belief that brain development ceases in early adulthood, research shows that the brain continues to develop and change throughout life. Neuroplasticity allows for ongoing learning, adaptation, and cognitive growth, emphasizing that the brain is capable of change and improvement well into old age.
Conclusion
The human brain is a marvel of complexity and adaptability, with numerous astonishing features that continue to fascinate scientists and researchers. From its incredible processing speed to its capacity for memory storage and predictive abilities, the brain remains one of the most intriguing and enigmatic organs in the human body. By understanding these mind-blowing facts, we can better appreciate the remarkable capabilities of the brain and continue to explore the mysteries of this extraordinary organ.